Set up active learning with Label Studio
Follow this tutorial to set up an active learning loop with Label Studio.
Use Label Studio Enterprise Edition to build an automated active learning loop with a machine learning model backend. If you use the open source Community Edition of Label Studio, you can manually sort tasks and retrieve predictions to mimic an active learning process. If you’re using Label Studio Community Edition, see how to manually manage your active learning loop.
About Active Learning
Creating annotated training data for supervised machine learning models can be expensive and time-consuming. Active Learning is a branch of machine learning that seeks to minimize the total amount of data required for labeling by strategically sampling observations that provide new insight into the problem.
In particular, Active Learning algorithms aim to select diverse and informative data for annotation, rather than random observations, from a pool of unlabeled data using prediction scores. For more about the practice of active learning, read this article written by our HumanSignal CTO on Towards Data Science.
Set up an automated active learning loop
Continuously train and review predictions from a connected machine learning model using Label Studio.
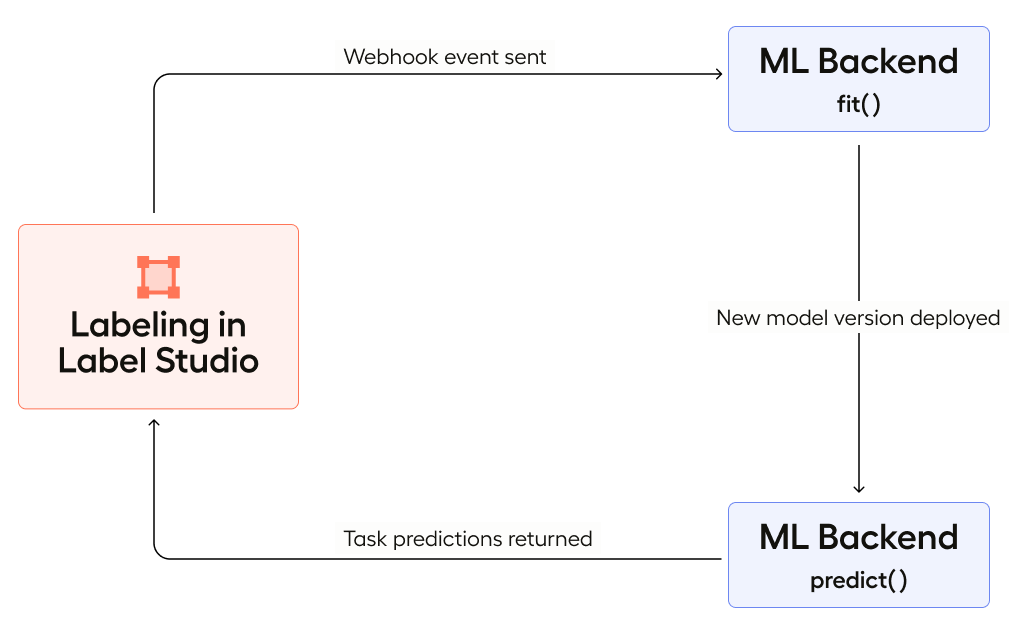
After a user creates an annotation in Label Studio, the configured webhook sends a message to the machine learning backend with the information about the created annotation. The fit() method of the ML backend runs to train the model. When the user moves on to the next labeling task, Label Studio retrieves the latest prediction for the task from the ML backend, which runs the predict() method on the task.
To set up this active learning, do the following:
- Set up an ML model as an ML backend for active learning.
- Connect the ML backend for getting predictions to Label Studio.
- Configure webhooks to send a training event to the ML backend (optional).
- Set up task sampling with prediction scores.
- Label the tasks.
As you label tasks, Label Studio sends webhook events to your machine learning backend and prompts it to retrain. As the model retrains, the predictions from the latest model version appear in Label Studio.
Set up an ML model as an ML backend for active learning
Set up an example machine learning model as an ML backend, or create a custom machine learning model.
Connect the ML backend to Label Studio for active learning
Follow the steps to connect a model to a Label Studio project and ensure the setting Start model training on annotation submission is enabled. This sends a training request to the backend after each annotation submission or update.
Configure webhooks to send a training event to the ML backend (optional)
By default, Label Studio notifies your ML backend every time an annotation is created or updated so that it can start training in response.
If you want, you can set up your project to send a webhook event and use that event and payload to drive event-specific training logic in your ML backend. If you want to customize the events and payloads sent to your ML backend, do the following:
- In the Label Studio UI, open the project that you want to use for active learning.
- Click Settings > Webhooks.
- Click Add Webhook.
- Add the following URL as your Payload URL:
http://localhost:9090/webhook - (Optional) Leave the option to Send payload enabled. The ML backend does not require a payload, but you can use it in your code to retrieve project-related details, such as the project ID that you can use to retrieve data, define training hyperparameters based on project settings, retrieve the project state, or other details.
- Disable the option to Send for all actions and enable Annotation created and Annotation updated.
- Click Add Webhook.
For more details on the webhook event payloads, see the full payload details for the annotation webhook.
Set up task sampling with prediction scores
In order to maximize the training efficiency and effectiveness of your machine learning model, you want your annotators to focus on labeling the tasks with the least confident, or most uncertain, prediction scores from your model. To do make sure of that, set up uncertainty task sampling.
Label the tasks
On the project data manager, select Label All Tasks to start labeling.
As your model retrains and a new version is updated in Label Studio, the tasks shown next to annotators are always those with the lowest prediction scores, reflecting those with the lowest model certainty. The predictions for the tasks correspond to the latest model version.
Customize your active learning loop
If you want to change the behavior of the active learning loop, you can make manual changes.
- Customize the prediction score produced by the model by modifying the inference call. See Make predictions with your ML backend for details and example code.
- To change the version of the model used to show predictions to annotators, update it in the machine learning settings. See Choose which predictions to show to annotators.
- If you want to delete all predictions after your model is retrained, see how to delete predictions.
- If you need to retrieve and save predictions for all tasks, see the recommendations for retrieving predictions from a model.
Set up manual active learning
If you’re using Label Studio Community Edition, data annotators can’t experience a live active learning loop. You can mimic an active learning experience by doing the following:
- Manually retrieve predictions from a model.
- Sort the tasks in the data manager by prediction score.
- Select Label Tasks As Displayed when labeling tasks.
This manual active learning loop does not automatically update the order of tasks presented to annotators as the ML backend trains with each new annotation and produces new predictions. Therefore, instead of on-the-fly automated active learning, you can perform a form of batched active learning, where you perform annotation for a period, stop to train the model, then retrieve new predictions and start annotating tasks again.