Fine-Tune an Agent with an LLM 🔒
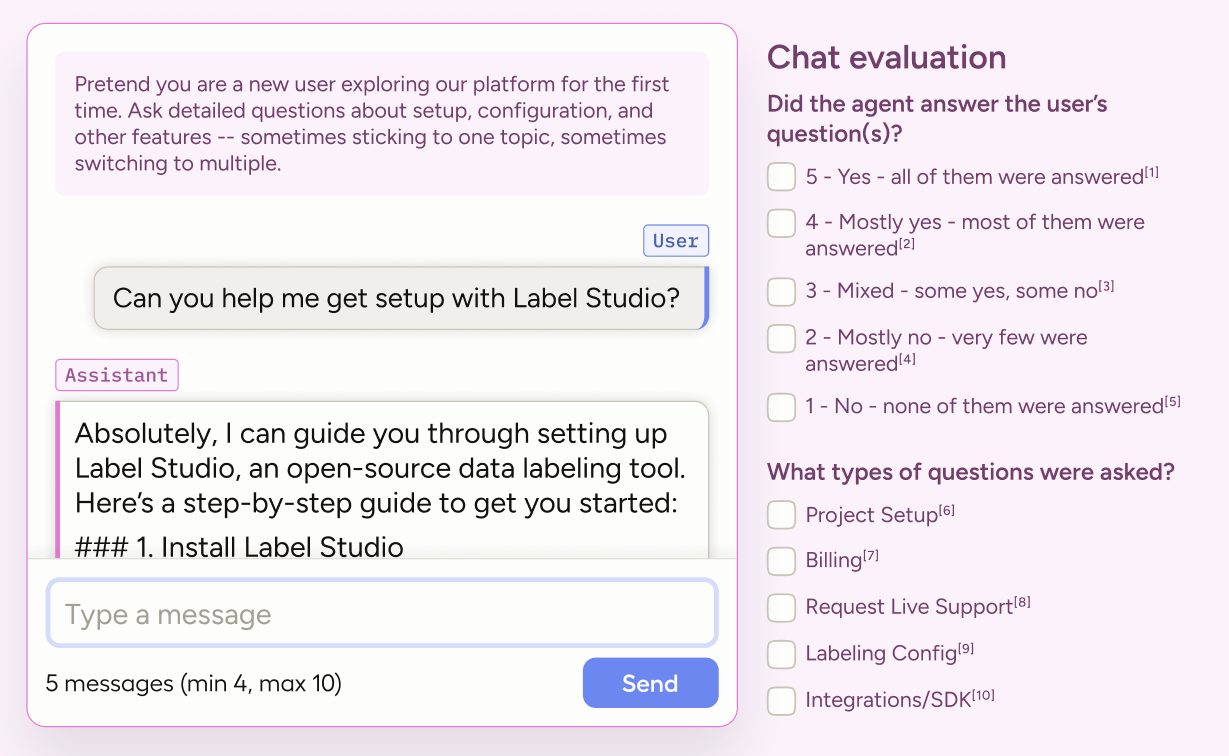
Run live, interactive chats with any OpenAI‑compatible LLM (including your own). Use this template to capture realistic, multi‑turn conversations for fine‑tuning. Help your agent specialize on key tasks, handle context shifts smoothly, and perform better under real‑world behavior.
While this template focuses on conversation-level evaluation, you can modify it to perform per-message evaluations. For examples, see our other chat templates.
Enterprise
This template requires Label Studio Enterprise.
Starter Cloud users can use the Chat tag, but have limited access to LLM integration. Instead, you can conduct a manual chat or import messages as predictions. See the Chat tag documentation.
For Community users, see our Conversation AI templates or the Multi-Turn Chat Evaluation template.
Labeling configuration
<View>
<Style>
.chat {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
<!-- Styling for evaluation panel on the right-->
.evaluation {
border: 2px solid var(--color-plum-800);
background-color: var(--color-plum-000);
color: var(--color-plum-900);
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
<!-- Styling for choices text color so that it is visible in dark mode-->
.evaluation .lsf-choices span {
color: var(--color-plum-900);
}
<!-- Styling for the instructions above the chat interface-->
.instructions {
color: var(--color-plum-900);
background-color: var(--color-plum-000);
padding-top: 15px;
padding-bottom: 15px;
}
<!-- Ensure submitted comment text is still readable in dark mode -->
[data-color-scheme="dark"] .lsf-row p {
color: var(--color-sand-100);
}
<!-- Allow enlarging the instruction text to better differentiate it-->
.lsf-richtext__container.lsf-htx-richtext {
font-size: 16px !important;
line-height: 1.6;
}
<!-- Remove excess height from the chat to allow space for instruction text -->
.htx-chat {
--excess-height: 300px
}
</Style>
<View style="display: flex; gap: 24px;">
<!-- Left: chat and instructions -->
<View className="chat" style="flex: 2;">
<View className="instructions">
<Text name="instructions" value="$text" />
</View>
<Chat name="chat" value="$chat"
llm="openai/gpt-4.1-nano"
minMessages="4"
editable="true" />
</View>
<!-- Right: conversation-level evaluation -->
<View style="flex: 1;" className="evaluation">
<Header value="Chat evaluation" size="2"/>
<Header value="Did the agent answer the user's question(s)?"/>
<Choices name="answered_rating" toName="chat" choice="single" showInline="true" required="true">
<Choice value="5 - Yes - all of them were answered"/>
<Choice value="4 - Mostly yes - most of them were answered"/>
<Choice value="3 - Mixed - some yes, some no"/>
<Choice value="2 - Mostly no - very few were answered"/>
<Choice value="1 - No - none of them were answered"/>
</Choices>
<Header value="What types of questions were asked?"/>
<Choices name="topics" toName="chat" choice="multiple" showInline="true">
<Choice value="Project Setup"/>
<Choice value="Billing"/>
<Choice value="Request Live Support"/>
<Choice value="Labeling Config"/>
<Choice value="Integrations/SDK"/>
<Choice value="Bug/Issue"/>
<Choice value="Other"/>
</Choices>
<Header value="Comments (optional)"/>
<TextArea name="comments" toName="chat" rows="4" placeholder="Add any notes or edge cases..."/>
</View>
</View>
</View>About this labeling configuration
This labeling configuration is divided into two columns with the chat interface on the left and conversation-level evaluation on the right.
Style
The styling is applied through <View> tags, which are rendered as HTML <div> tags.
You can apply styling using inline styles directly on View tags or by defining CSS rules for classes in a <Style> block. Those classes are then applied within the labeling configuration using the className parameter.
For example, this View tag uses a combination of inline styles and className:
<View className="chat" style="flex: 2;">The CSS rules for the .chat class are defined with the <Style> block.
Tip
.htx-chat is a special Label Studio class that allows you to control the height of the chat portion of the interface.
For more information, see the Style tag.
Text
Above the chat there are instructions guiding the user as to what they should try to achieve with the text.
You can hard-code this into the labeling configuration (<Text value="Your instruction text" />), but if you are going to have multiple tasks within a project, you will likely want to specify the text as part of the imported data.
In this example, we use $text because the input JSON uses "text". See input data below.
For more information, see the Text tag.
Chat
The Chat tag provides an interface where the annotator can type and send messages.
<Chat name="chat" value="$chat"
llm="openai/gpt-4.1-nano"
minMessages="4"
editable="true" />name: This is required, and when you want your control tags (choices, ratings, etc) to reference the chat element, you point to it usingtoName="chat". You can use whichever name you like when customizing your own labeling configurations.value: This is required, and should use a variable referencing your input data. In this example, we use$chatbecause the input JSON uses"chat".llm: Messages from the annotator will be sent to an LLM and the response returned within the chat area of the labeling configuration. For more information, see Chat tag - Use with an LLM.minMessages: The minimum number of messages users must submit to complete the task. You can also set a maximum.Both minimum and maximum can also be set in the task data, allowing you to have different limits for each task. For an example, see Chatbot Evaluation.
editable: Messages from the annotator and from the LLM are editable. To modify this so that only messages from certain roles are editable, you can specify them (for example,editable="user,assistant").
For more information and additional parameters, see the Chat tag.
Choices and TextArea
In this template, the evaluation options are applied to the entire chat. For examples of per-message evaluation, see Chatbot Evaluation, LINK, LINK.
For more information about modifying these options, see the Choices tag and TextArea tag.
Input data
The Chat tag accepts JSON data.
Empty chat
The following would provide an empty chat window and instruction text for the annotator:
{
"data": {
"text": "Pretend you are a new user exploring our platform for the first time. Ask detailed questions about setup, configuration, and other features -- sometimes sticking to one topic, sometimes switching between multiple. Make the conversation realistic, as if you are trying to get actual work done.",
"chat": []
}
}Imported chat messages
You can also import demo chat messages as follows:
{
"data": {
"text": "Pretend you are a new user exploring our platform for the first time. Ask detailed questions about setup, configuration, and other features -- sometimes sticking to one topic, sometimes switching between multiple. Make the conversation realistic, as if you are trying to get actual work done.",
"chat": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Demo chat message 1"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Demo chat message 2"
},
{
"role": "developer",
"content": "Demo chat message 3 "
}
]
}
}attention
The chat messages that you import are not selectable. This means that you cannot edit them or apply annotations (ratings, choices, etc) to them.
You can only select and annotate messages that are added to the chat by an annotator or that are imported as predictions.