Review annotations in Label Studio
After multiple labelers have annotated tasks, review their output to validate the quality of the results. You can also perform this task after a model has predicted labels for tasks in your dataset. To configure the settings for reviewing annotations, see Set up review settings for your project.
The annotation review workflow is only available in Label Studio Enterprise Edition. If you’re using Label Studio Community Edition, see Label Studio Features to learn more.
See the following video for an overview of reviewer workflows:
Why review annotations?
Data labeling is a crucial step for training many machine learning models, and it’s essential to review annotations to make sure that only the highest quality data is used to train your machine learning model. If you don’t review the quality of labeled data, weak annotations might be used when training your model and degrade overall model performance.
Review annotated tasks
After you assign reviewers to tasks, they can review annotated tasks. Administrators and project managers can review tasks at any time, without being added to a project.
Reviewers can click Review Annotations for a specific project, then click Review All Tasks on the Data Manager to start reviewing tasks. Administrators and project managers can click tasks from the Data Manager or Explore Review.
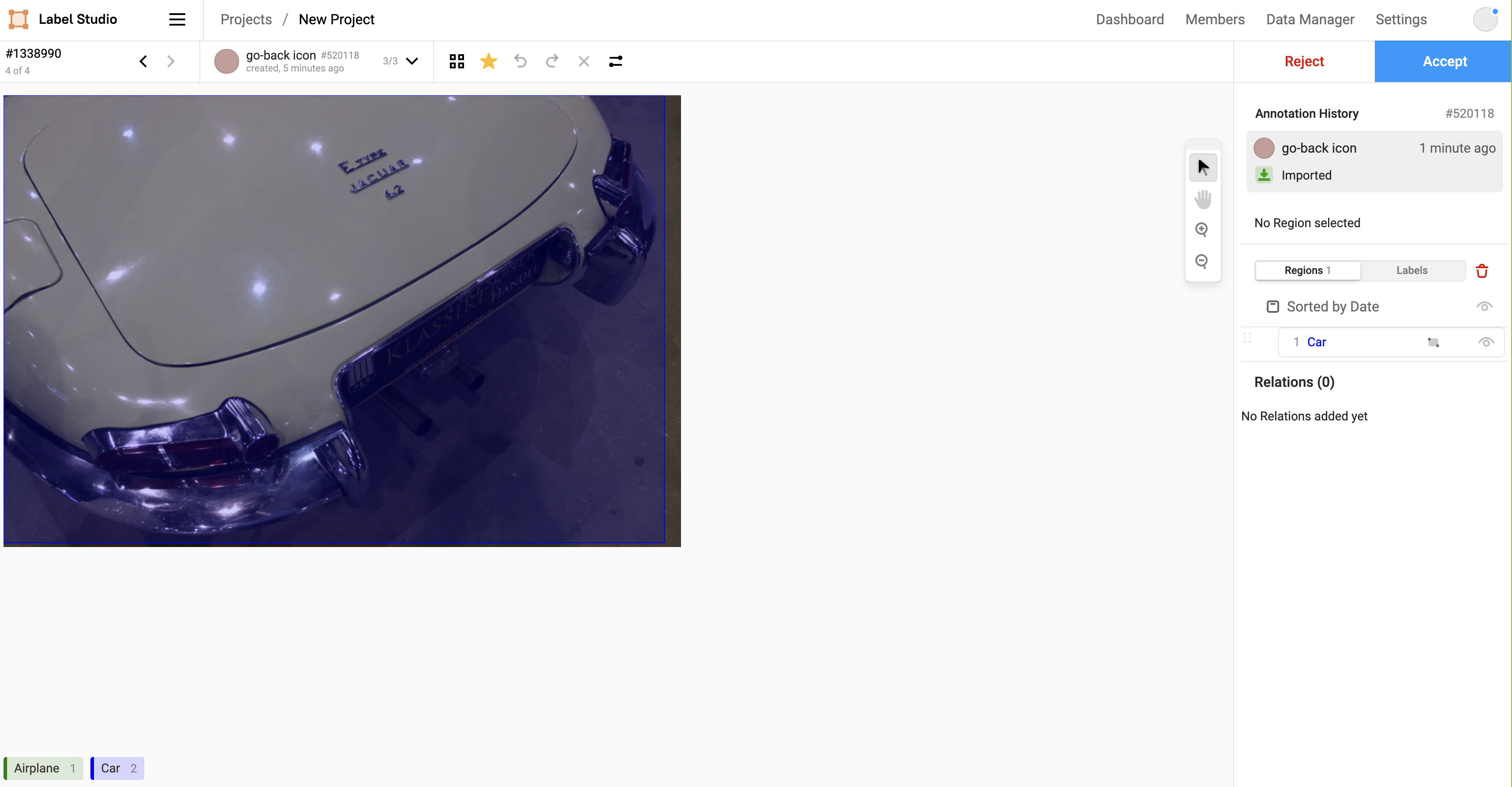
Review the first task and annotation.
By default, you view the tasks in the order in which they were presented to the annotator. If you want to change the order that you review tasks, see Choose what to review.
If the annotation is correct, click Accept.
If the annotation is mostly correct, you can correct it by selecting a different option, changing the selected region, moving the bounding box, or whichever makes sense for the type of label you’re reviewing. After correcting the annotation, click Fix & Accept.
If the annotation is completely incorrect, or you don’t want to attempt to correct it at all, click Reject to reject the annotation. To place a rejected task back in the Label Stream for annotation, you must delete the annotation. Rejecting an annotation does not return it to annotators to re-label.
Continue reviewing annotated tasks until you’ve reviewed all annotated tasks. Click Data Manager to return to the list of tasks for the project.
Tip
If there are multiple annotations, you can select the tab of each annotation by annotator and result ID to view them separately. The annotation result ID is different from the task ID visible in the left menu. To see annotations side-by-side, you can click the task in the Data Manager and view a grid of annotations in the task preview mode.
Choose what to review
You can review tasks in random order, or order tasks in the project data manager in different ways, depending on your use case:
- Order tasks by annotator, to review annotations and assess individual annotator performance at the same time.
- Order tasks by agreement, to review annotations with more uncertainty among annotators first.
- Order tasks by model confidence score, to review the annotations that a machine learning model was less certain about first.
Task ordering and limiting (Enterprise)
For Label Studio Enterprise projects, you can configure the review stream ordering and limit the review slice:
- Task Ordering: Choose between By Task ID (sequential) and Random. Random preserves the order of annotations within each task but randomizes task order.
- Task Limit (%): When Random is selected, optionally limit the percentage of project tasks available for review. The limit is applied after any filters such as “Show only finished tasks.” When reviewers start a review session from a Data Manager selection (selected items), the limit is bypassed for that session.
See Settings > Review > Task Ordering and Task Limit for configuration details.
Navigate between tasks or annotations
You can now navigate back through the review stream in the same path as moving forward when Task is reviewed after all annotations are reviewed option is set. The go back (<)functionality takes you back through the same set of annotations as it had moving forward.
As an ADMINISTRATOR, log in to the Label Studio app.
Navigate to All Projects page, if needed.
Open any project.
Observe that you are taken to Data Manager.
Navigate to Settings >> Review.
Select
Task is reviewed after all annotations are reviewedoption.Click SAVE button.
Navigate back to Data Manager.
Make sure to have several tasks set up with exactly two annotations each, but no reviews.
Click REVIEW ALL TASKS button.
Observe that you are taken to Review Stream.
Note the task or annotation that you are on.
Complete review for this annotation.
Observe that you are taken to same task (second annotation).
Repeat steps 12 to 14 for couple more times.
Navigate back through the Review Stream using the go back (
<) button.
note
Confirm that you are not taken through the same path that you have come through moving forward.
Assign reviewers to tasks
As an administrator or project manager, you can assign reviewers to tasks, or people with access can review tasks on an ad hoc basis. Anyone who is assigned to a task or who completes a review of a task appears in the Reviewers column on the Data Manager. You must first add a reviewer to the project or add members to the project workspace before you can assign them as a reviewer.
- For a specific project, select tasks on the Data Manager.
- Select the tasks dropdown and select Assign Reviewers.
- Select names of reviewers and click the
>arrow to assign them to the selected tasks. - Click Assign.
You can assign reviewers to multiple tasks at once, but you cannot remove reviewers from multiple tasks at once.
Review annotator activity on the project dashboard
Use the project dashboard to review annotator activity. For a project, click Dashboard to view the dashboard.
If you don’t see an annotator’s activity reflected on the dashboard, make sure they have been added as a member to the project.
Review label distribution
For specific labels, you can see in a donut chart how many labels of each type were applied to the tasks. Use this chart to identify possible problems with your dataset distribution, if some labels are overrepresented in an annotated dataset compared with others.
For example, if you’re developing a dataset of OCR images, and 90% of your tasks have Text labels and 10% have Handwriting labels, you might want to increase the number of images of handwriting in your dataset, to improve the eventual accuracy of a machine learning model trained on this dataset.
Pause an annotator
For organizations with a large number of annotators, it might prove useful to pause an annotator’s progress. This might be helpful for annotators that are performing poorly or exhibiting behavior that might indicate they have automated their work (bot behavior).
Manually pause an annotator
You can manually pause annotators from the Members dashboard in a project. This action is only available next to users in the Annotator and Reviewer roles:
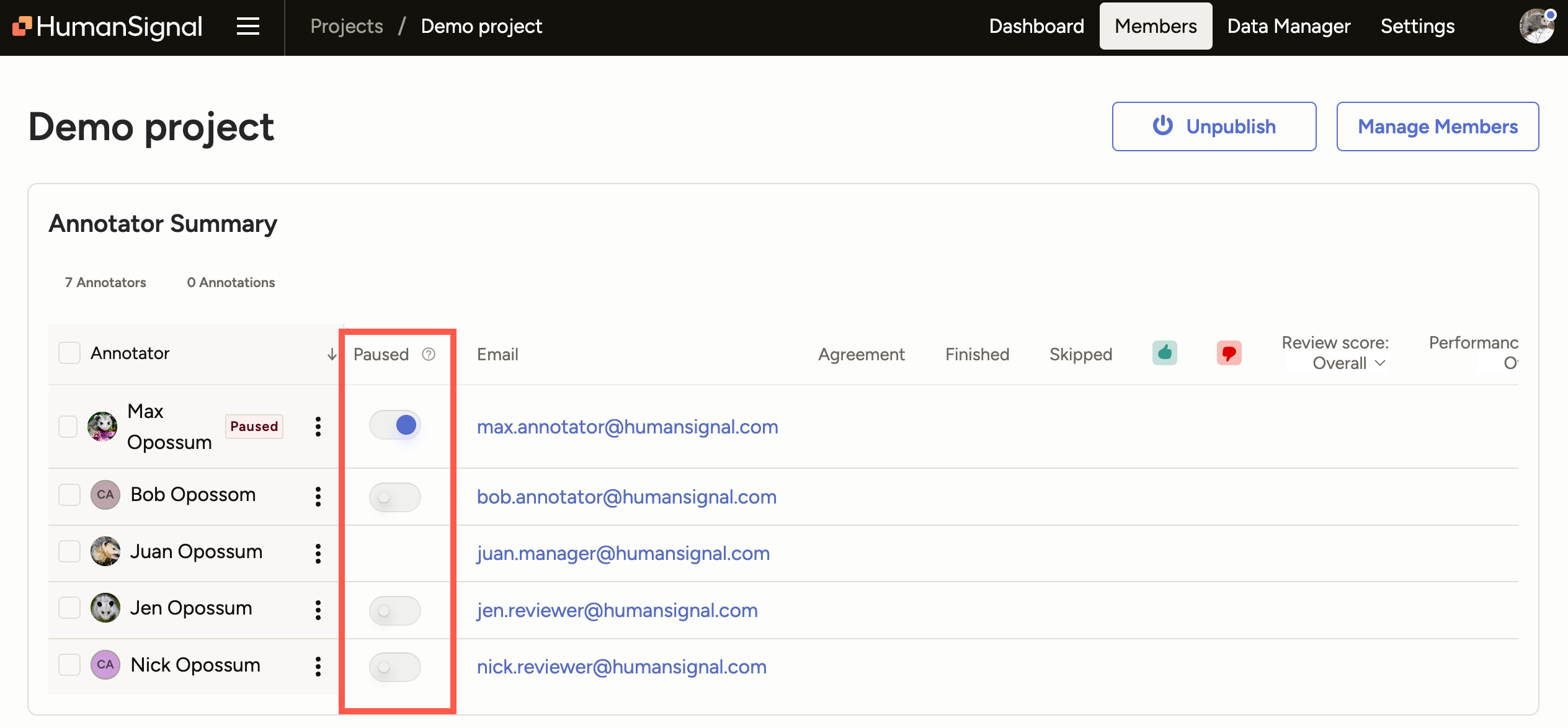
When a user is paused, the following occurs:
They immediately see a message informing them that they have been paused.

Their progress within their current task is saved as a draft, but they cannot make any further changes.
When they click Go Back, they are returned to the Projects page. If they attempt to re-enter the project, they are shown the error message above.
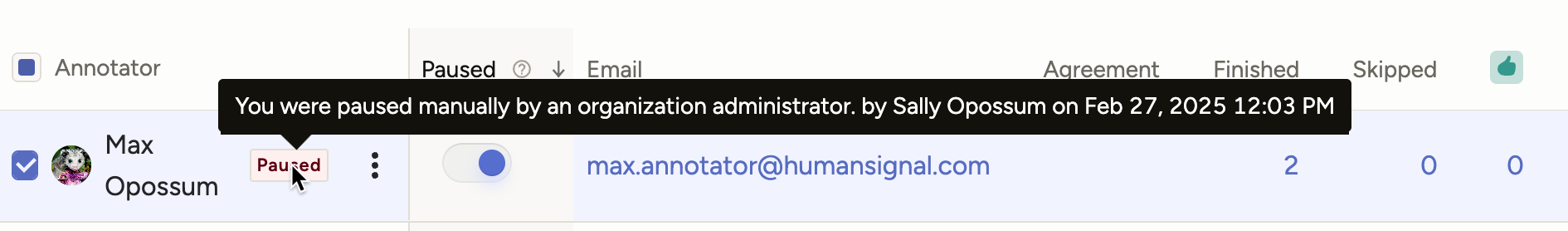
Tip
If you hover over the Paused indicator, you can see the message that was shown to the user when they were paused. If a user was manually paused, it also shows who initiated the action.
Automatically pause annotators
Annotation Limit settings
You can use Settings > Quality > Annotation Limit to set limits on how many tasks an annotator is able to complete before they are paused. For more information, see Annotation Limit.
Behavior-based triggers
If you have plugins enabled, you can automatically pause an annotator based on certain behaviors and then customize the message that appears on their screen.
For more information, see Plugins - Spam and Bot Detection.
Verify model and annotator performance
To verify the performance of specific annotators, review the Members section for a specific project. If you don’t see an annotator’s activity reflected, make sure they have been added as a member to the project.
Review annotator performance
For each project, you can review the project dashboard and review the Annotator Performance section to learn more about the annotators and their annotations, as well as overall annotator consensus.
Discover how many annotators have worked on the project, and how many hours they cumulatively spent labeling. You can also see the total number of annotations produced by the annotators, separate from the total number of tasks in the project.
Review a table to see the following for each annotator:
- The total agreement for one annotator with all other annotators. See more about how annotator agreement is calculated.
- The number of tasks that they finished annotating.
- The number of tasks that they skipped.
- The outcome of reviews for the annotations they performed.
- The total annotation progress across all tasks in the project.
- The mean time to annotate the tasks. Select this header to view the
median timeinstead. Mean time and median time are calculated using the total time spent on each task by an annotator, including idle time. - The agreement of their annotations with the ground truth annotations, if there are any.
- The agreement of their annotations with predicted annotations, if there are any.
See the following video for an overview of annotator agreement metrics:
Review annotator agreement matrix
You can also review the overall annotator agreement on a more individual basis with the annotator agreement matrix.
Review the annotator agreement matrix to understand which annotator’s annotations consistently agree with or don’t agree with other annotator’s annotations. You can also filter the matrix to show specific agreement statistics for each label, or view the Overall agreement matrix. See more about how annotator agreement is calculated.
To see the specific annotations contributing to the agreement, do the following:
- Open the Data Manager for the project.
- Locate a task annotated by the different annotators that you want to compare.
- Click the task to open the task preview.
- Click each annotation tab to compare how the different annotations differ. The initials of each annotator appears in the tab header with the annotation ID.
Review agreement distribution across tasks
You can also review the distribution of agreement percentages across project tasks. A bar chart depicts the number of tasks with a specific agreement percentage. The more tasks with higher agreement, the higher quality your dataset is likely to be. Clusters of agreement percentages for specific tasks might mean that some tasks are easier to label than others, while other tasks are more confusing and difficult to label consistently.
Review annotations against ground truth annotations
Define ground truth annotations in a Label Studio project. Use ground truth annotations to assess the quality of your annotated dataset. Review ground truths to make sure that annotators are accurately labeling data at the start of the project, and continually throughout the lifecycle of the training dataset creation.
Label Studio Enterprise compares annotations from annotators and model predictions against the ground truth annotations for a task to calculate an accuracy score between 0 and 1.
note
Ground truth annotations are only available in Label Studio Enterprise Edition. If you're using Label Studio Community Edition, see Label Studio Features to learn more.
Define ground truth annotations for a project
Set specific task annotations as ground truth annotations from the Data Manager page for a project.
- Locate the task that you want to set a ground truth annotation for.
- Click the task to preview all annotations for the task as tabs. If an annotation is already set as a ground truth, the annotation ID in the tab has a yellow star next to it.
- In the annotation sidebar for the task, click the star icon next to the annotation ID to set the annotation result as a ground truth.
A task can only have one annotation set as the ground truth annotation for the task. If you set a new annotation for a task as a ground truth, the previous annotation for that task set as a ground truth is updated to no longer be a ground truth annotation.
Manage ground truth annotations for a project
Review and modify the ground truth annotations for a project.
Review existing ground truth annotations
You can adjust the Data Manager columns to show whether a task has any annotations set as ground truth annotations.
- On the Data Manager, select the Columns drop-down menu.
- Select the checkbox for Ground Truth. A column appears with a star icon and true or false values listed for tasks, indicating whether a ground truth annotation has been set for a task.
- Click Columns again to close the menu.
You can also filter the Data Manager to show only tasks with ground truth annotations so that you can review them.
- On the Data Manager, select the Filters drop-down menu.
- Click + Add Filter and select where Ground Truth is yes. The Data Manager updates to show only tasks with ground truth annotations set.
- Click Filters again to close the menu.
Remove ground truth annotations
To remove ground truth annotations,
- When viewing the data manager for a project, select the checkboxes next to annotated tasks.
- In the selected tasks dropdown menu, select Delete ground truths. This does not delete the annotation, but changes the status of the ground truth setting for the annotation to false.
You can also remove ground truths when you annotate a task.
- When labeling a task, create an annotation or select an existing one.
- Click the star icon to unset the annotation result as a ground truth.